About Us
Truck Fuel Injectors: The "Precise Valve" for Engine Fuel Supply
Views : 174
Update time : 2025-07-17 11:40:25
I. Introduction
In the fuel supply system of a truck engine, the fuel injector is a "precise valve" whose condition is directly related to fuel combustion efficiency, power output, and exhaust emissions. Understanding its characteristics and maintenance points is essential for ensuring the efficient and economical operation of the truck.
II. Core Role of Truck Fuel Injectors

The fuel injector sprays fuel into the combustion chamber with specific pressure, angle, and atomization state, and needs to precisely control three parameters: injection quantity (matching engine load), injection timing (coordinating with piston movement to improve efficiency), and atomization effect (increasing contact area with air and reducing emissions). The working pressure of diesel engine fuel injectors usually reaches hundreds of bars, and precise control under high-pressure environment is particularly important, directly affecting the fuel economy and power performance of the truck.
III. Structure and Types of Truck Fuel Injectors
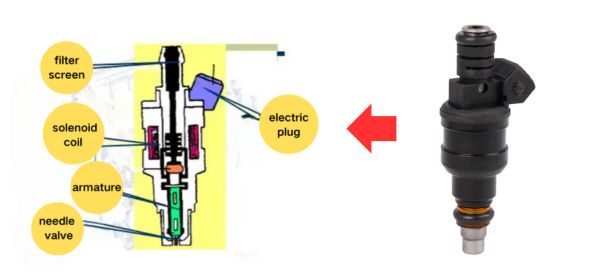
(I) Basic Structure
It mainly consists of injector body, needle valve pair (core precision component with a matching gap of 0.001-0.003mm), spring, armature (for electronic control type), etc. The spring controls the opening and closing of the needle valve, and the electromagnetic coil or piezoelectric crystal in the electronic control fuel injector realizes millisecond-level control through electrical signals.
(II) Common Types
- Mechanical fuel injectors: Rely on the pressure of the high-pressure fuel pump, with parameters controlled by a mechanical governor. They are simple in structure, low in cost, but have limited precision, mostly used in old trucks.
- Electronic control fuel injectors: Divided into solenoid valve type and piezoelectric type, controlled by the ECU according to sensor signals. Piezoelectric ones have faster response, can achieve multiple injections, reduce noise and emissions, and are widely used in modern heavy trucks.
IV. Common Faults and Diagnosis of Fuel Injectors
(I) Typical Fault Manifestations
- Poor atomization: Fuel is sprayed in a column instead of mist, resulting in insufficient combustion, leading to reduced power, increased fuel consumption, and black smoke.
- Leakage: Poor sealing of the needle valve causes fuel dripping, leading to unstable idling, difficulty in starting, and possible damage to the three-way catalyst.
- Blockage: Impurities or carbon deposits block the injection holes, reducing injection quantity or shifting the angle, causing engine jitter and weak acceleration.
(II) Fault Causes and Diagnosis
- Causes: Poor fuel quality exacerbates wear and blockage; long-term low-speed or idle operation easily causes carbon deposition; overpressure operation leads to spring fatigue or needle valve jamming.
- Diagnostic methods: Read injection data with a special diagnostic instrument; observe exhaust color (black smoke indicates poor atomization, white smoke may indicate leakage); disassemble to check the needle valve and injection holes.
V. Daily Maintenance Strategies for Fuel Injectors
- Use high-quality fuel: Choose regular fuel, replace the fuel filter regularly to reduce impurities entering.
- Regular cleaning: Use cleaning agents or disassemble for cleaning at 20,000-30,000 kilometers to remove carbon deposits.
- Standard operation: Avoid long-term idling or sudden acceleration and deceleration; start the engine after the water temperature is normal when cold.
- Timely maintenance: Check in time when power and fuel consumption are abnormal, and replace parts if necessary to avoid expanding faults.
VI. Conclusion
Truck fuel injectors are the "precision stewards" of the engine fuel system, and their performance determines the power, economy, and environmental protection of the engine. Mastering their structure, principle, and maintenance points can solve problems in time, extend engine life, reduce operating costs, and ensure efficient operation of trucks.
相关新闻
 Revealing Three Little-Known Facts About Trucks
Revealing Three Little-Known Facts About Trucks
Aug 06,2025
This article presents three little-known facts about trucks, including that the cab can be flipped for engine maintenance, the rearview mirrors are equipped with defrosting and deicing functions, and the small tank next to the fuel tank is an urea tank which is crucial for environmental protection. It helps readers understand the secrets behind truck designs and functions.
 Control Valve: The "Key Steward" in Truck Engines
Control Valve: The "Key Steward" in Truck Engines
Aug 05,2025
This article introduces the role of the control valve in the diesel pump, including controlling fuel quantity and stabilizing pressure; lists symptoms when it malfunctions, such as weakened power and increased fuel consumption; provides maintenance methods, and illustrates through cases that paying attention to the control valve can avoid unnecessary expenses.
 Control Valve: The "Invisible Commander" of Truck Power
Control Valve: The "Invisible Commander" of Truck Power
Aug 05,2025
The control valve is an indispensable core regulating component in the truck power system. Although it hides inside the machinery and keeps a low profile, it relies on its powerful functions to precisely command the rhythm of power output, comprehensively ensure driving safety, and intelligently adapt to various working conditions. With sophisticated design techniques and durable material selection, it can achieve a perfect balance between power and efficiency in various complex scenarios, and can be called the invisible cornerstone supporting the efficient and stable operation of trucks.
 Truck Snow Chains: Safety Guarantee on Icy and Snowy Roads
Truck Snow Chains: Safety Guarantee on Icy and Snowy Roads
Jul 28,2025
This article elaborates on truck snow chains, including their important role on icy and snowy roads, applicable scenarios, selection methods, installation steps, and usage precautions. It aims to provide references for truck drivers to drive safely in icy and snowy weather and reduce accidents caused by slippery roads.
